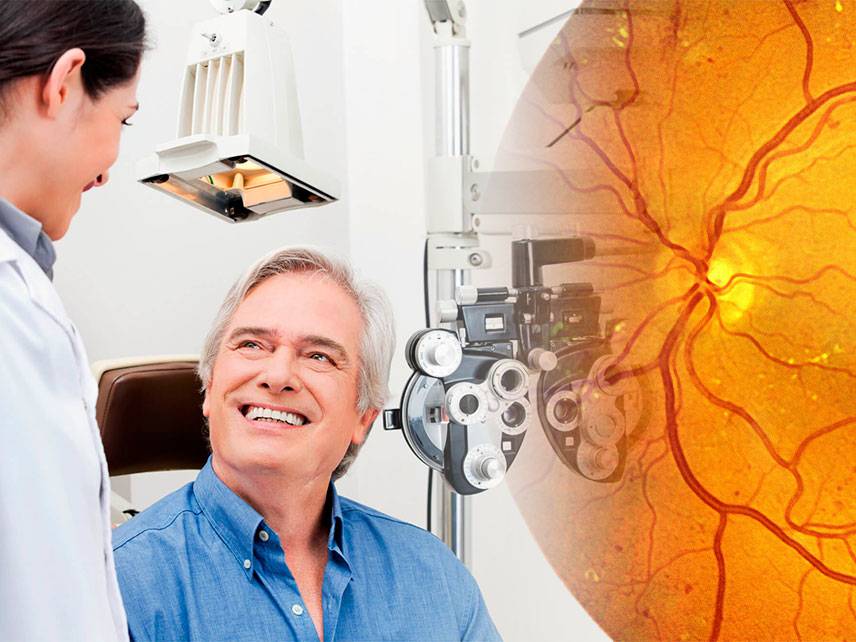
Diabetic retinopathy is a common eye condition that is caused by diabetes and affects the back of the eye, known as the retina. It can lead to a permanent loss of vision if not treated. The condition develops slowly and may not cause any symptoms in the early stages. However, it can worsen over time and cause vision loss.
Signs and Symptoms
In the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, there are often no symptoms. As the condition progresses, it can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
-
Blurred vision
-
Difficulty seeing at night
-
Seeing spots or floaters
-
Having a dark or empty spot in the center of your vision
-
Having tunnel vision
-
Having fluctuating vision
Causes
Diabetic retinopathy is caused by changes in the blood vessels of the retina due to diabetes. The high levels of sugar in the blood cause the blood vessels to become weak, swell, and leak. This can cause vision loss.
Risk Factors
The risk of developing diabetic retinopathy increases with the duration of diabetes. It can also be increased by:
-
Poorly controlled blood sugar levels
-
High blood pressure
-
High cholesterol levels
-
Smoking
-
Pregnancy
Prevention
The best way to prevent diabetic retinopathy is to keep your blood sugar levels in check. This can be done by eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking any prescribed diabetes medications. Additionally, reducing your risk factors, such as quitting smoking, controlling your blood pressure and cholesterol, and getting regular eye exams can help prevent the condition.
Diagnosis
Diabetic retinopathy can be diagnosed using an ophthalmologic exam. During the exam, the doctor will use a device called an ophthalmoscope to look inside the eye and look at the retina. The doctor may also take photos of the retina to look for signs of damage.
Treatment
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the severity of the condition. If the condition is mild, the doctor may recommend that you monitor your vision regularly and make lifestyle changes to reduce your risk factors. If the condition is more severe, the doctor may recommend laser surgery to seal leaking blood vessels or injections of drugs to reduce swelling in the retina.
Coping and Support
If you have been diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy, it is important to seek emotional and practical support. Support groups can be an invaluable source of information and comfort. Additionally, talking to a therapist or counselor can help you learn how to cope with the condition and make lifestyle changes to reduce your risk.
Complications
Diabetic retinopathy can lead to a variety of complications, including:
-
Blindness
-
Glaucoma
-
Cataracts
Living with Diabetic Retinopathy
Living with diabetic retinopathy can be difficult, but there are things you can do to manage the condition. It is important to keep your blood sugar levels in check and make lifestyle changes to reduce your risk factors. Additionally, regular eye exams are key to catching any changes in your vision. With the right care and support, you can live a full and active life with diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that can lead to permanent vision loss if not treated. It is important to make lifestyle changes to reduce your risk and get regular eye exams to catch any changes in your vision. With the right care and support, you can live a full and active life with diabetic retinopathy.