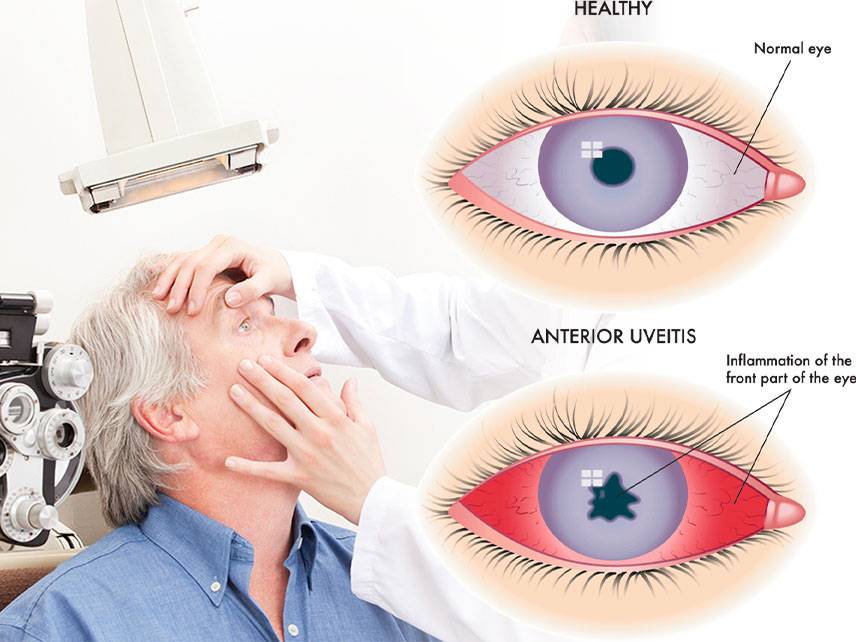
Uveitis is an inflammation of the eye’s uvea, the layer between the white of the eye (sclera) and the retina. It can be caused by a wide range of infectious and noninfectious conditions. Uveitis is one of the leading causes of blindness if not treated quickly.
Signs and Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of uveitis are typically related to the underlying cause.
Symptoms may include:
-
Redness
-
Eye pain
-
Blurred vision
-
Light sensitivity
-
Floaters
-
Dark or blurry spots in your field of vision
Causes
Uveitis has many possible causes, including:
-
Infections, including viruses, bacteria and fungi
-
Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and ankylosing spondylitis
-
Injury or trauma to the eye
-
Certain medications
-
Tumors
-
Parasites
-
Inflammatory conditions, such as sarcoidosis
Risk Factors
Certain people are at greater risk of developing uveitis, including:
-
People with a family history of uveitis
-
People with certain autoimmune diseases
-
People who have had surgery or an eye injury
-
People with certain infections, such as tuberculosis and herpes
Prevention
There is no sure way to prevent uveitis.
However, if you are at risk for developing the condition, you can take measures to reduce your risk, including:
-
Getting prompt treatment for any infections or injuries
-
Eating a healthy diet
-
Getting regular exercise
-
Not smoking
-
Taking measures to prevent eye injuries
Diagnosis
To diagnose uveitis, your doctor will likely:
-
Do a physical exam
-
Perform tests to measure your vision
-
Perform eye tests, such as an eye exam and imaging tests
-
Take a sample of the fluid in your eye to test for infection
-
Check for signs of inflammation in the blood
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation and prevent vision loss.
Treatment may include:
-
Eye drops or ointments to reduce inflammation
-
Corticosteroid injections
-
Oral corticosteroid medications
-
Antibiotics to treat infection
-
Immunosuppressants to treat autoimmune diseases
Coping and Support
It can be difficult to cope with the diagnosis of uveitis and the associated vision loss.
If you are struggling to cope, it can be helpful to:
-
Reach out to family and friends for emotional support
-
Talk to a counselor or therapist
-
Join a support group
-
Learn more about uveitis and how to manage it
Complications
Uveitis can lead to serious complications, including:
-
Vision loss
-
Cataracts
-
Glaucoma
-
Retinal detachment
-
Macular edema
Living with Uveitis
Living with uveitis can be challenging. It is important to take measures to protect your vision, such as wearing sunglasses when outdoors and avoiding contact sports. You should also follow your doctor’s instructions and take all prescribed medications as directed. Finally, be sure to attend all follow-up appointments and have regular eye exams to monitor your condition.
Uveitis can be a serious condition, but with prompt diagnosis and treatment, it can often be managed and vision loss can be prevented. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of uveitis, it is important to see your doctor right away.