Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a degenerative eye disease that affects the macula, the part of the eye responsible for sharp, central vision. It is the leading cause of vision loss among people over the age of 65 and affects more than 10 million Americans. AMD is a chronic condition, meaning that it progresses slowly over time, and can lead to severe vision loss if not treated.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptoms of AMD include blurred or distorted central vision, difficulty reading or recognizing faces, and difficulty with tasks that require fine vision, such as threading a needle or driving. In addition, some people experience decreased color vision or a darker or lighter area in the center of their vision field.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of AMD is unknown, but there are several known risk factors, such as age, genetics, smoking, and exposure to UV light. Other risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and obesity.
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent AMD, but there are some steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing the disease. These steps include quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and wearing sunglasses to protect the eyes from UV light.
Diagnosis
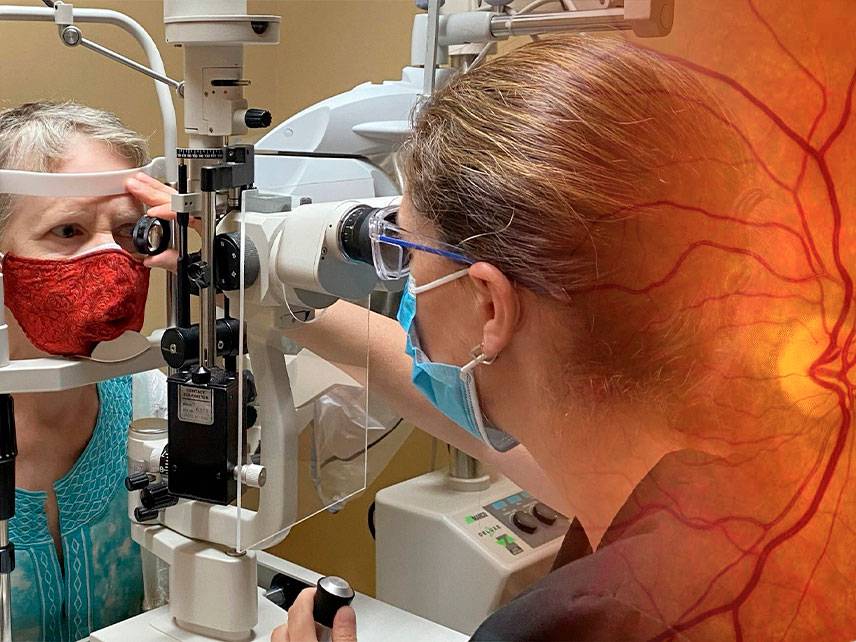
AMD is typically diagnosed during an eye exam. During the exam, the doctor will check the eye's retina and macula for any signs of damage or deterioration. The doctor may also perform other tests, such as an Amsler grid test or an OCT scan, to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
The treatment for AMD depends on the type and severity of the condition. For early stages of AMD, treatment may include lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and eating a healthy diet. In more advanced stages, treatment may include medications, such as anti-VEGF injections, which can slow the progression of the disease. Surgery may also be an option for some people with AMD.
Coping and Support
Living with AMD can be difficult, but there are ways to cope with the condition. It is important to stay informed about the latest treatments and research, and to take steps to maintain good eye health. In addition, support groups and counseling can help people with AMD cope with the emotional and social aspects of the disease.
Complications
AMD can lead to serious complications, such as blindness, if it is not treated. In addition, people with AMD may be at increased risk of falls, due to decreased vision.
Living with Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Living with AMD can be difficult, but there are steps you can take to maintain good eye health and reduce the risk of complications. These steps include quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and wearing sunglasses to protect the eyes from UV light. In addition, keeping up with regular eye exams can help to detect any changes in vision early, and allow for timely treatment.
Age-related macular degeneration is a serious condition that can lead to significant vision loss if not treated. While there is no cure for AMD, there are treatments available that can help to slow the progression of the disease and maintain good vision. With the right treatment and lifestyle modifications, people with AMD can live full, active lives.